企業永續:從「心」啟航
Business Sustainability: A Journey from the Heart
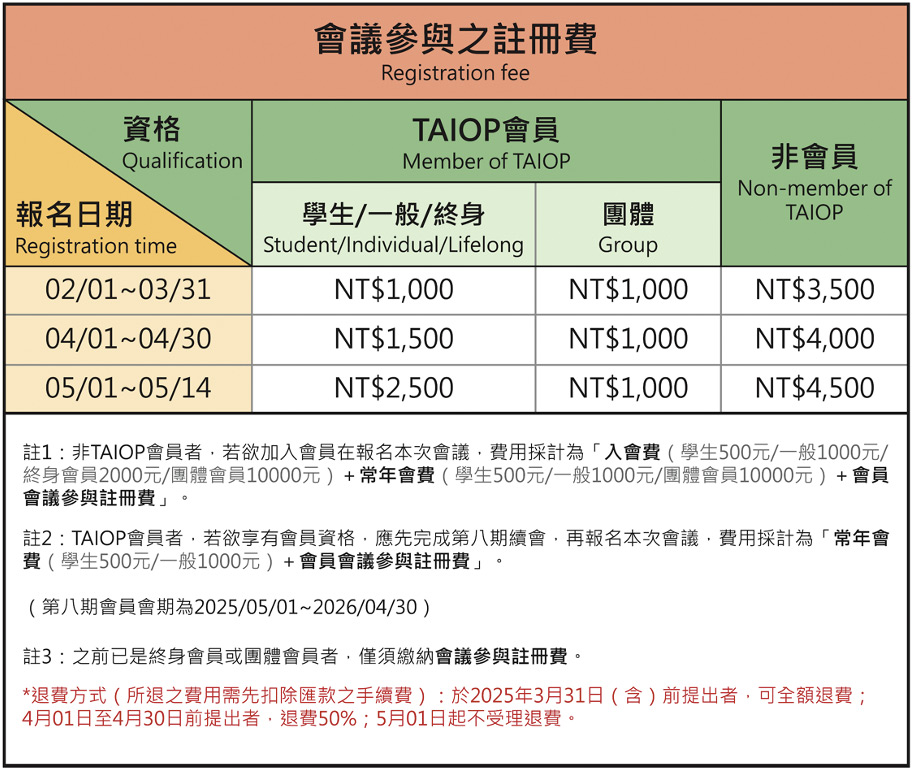
會議時間 Dates
2025/5/17(六)、2025/5/18(日)
會議地點 Venue
國立臺灣大學
應用力學館
主辦單位 Organizer
社團法人臺灣工商心理學學會
國立臺灣大學心理學系
協辦單位 Co-organizer
中原大學心理學系
國立政治大學心理學系
國立政治大學企業永續管理研究中心
贊助單位 Sponsors
國家科學及技術委員會
環顧全球現況,人們正面臨著貧困、氣候變遷,以及種族性別歧視所帶來的各種挑戰。為了因應這些挑戰,聯合國於2015年設立了17項永續發展目標(Sustainable Development Goals,SDGs),希望能彙整各國資源、團結政府民間力量,一同建構符合全球共同利益的永續發展模式。聯合國認為,永續發展模式應是「以不拋下任何人為原則,在滿足現今需求的同時,也滿足後代子孫需求的發展模式」,此與過往強調經濟成長、重視當前享樂的發展模式大不相同。因此,為了建構足以實踐SDGs的永續發展模式,除了各國政府得重新審視追求經濟發展的政策是否合宜之外,私人企業能否從獨重獲利的營運模式,轉型為兼顧經濟目標、社會包容及環境保護的永續營運模式,亦是不容忽視的重要關鍵。
受到此一趨勢的影響,企業藉由聚焦於環境、社會及治理(Enivronment, Social and Governance,ESG)三項管理指標,響應並實踐SDGs所描繪的永續願景。環境關注企業是否在追逐利益的同時,也注重維護環境與促進友善環境之行為。社會關注企業是否重視勞工權益,確保任何身份背景的員工,都能獲得公平對待,而沒有歧視、壓榨及不當雇用之狀況。治理關注企業高階管理團隊是否遵守法令,並秉持誠實透明的原則,揭露必要且重要之資訊。隨著永續發展逐漸成為共通價值,違背ESG的企業不僅將失去利害關係人的信任,其品牌形象亦會蕩然無存,導致企業蒙受巨大損失。舉例來說,許多金融機構訂定規範,禁止旗下銀行融資或投資違背ESG的企業;此外,消費者亦會透過抵制行為,抗議破壞環境、侵犯勞權或隱瞞貪腐的企業。實際上,諸如Google、聯合利華(Unilever)及Toyota等等,都致力於推動ESG的相關政策與實務,說明了遵循ESG已是企業營運的關鍵因素。
值得注意的是,員工是否認同永續價值,進而願意採行符合ESG原則的永續發展行為,是企業能否建構永續營運模式的重要關鍵。進一步來說,如何激勵與引導員工認同並達成ESG所提倡的管理目標,不僅是不容迴避的管理議題,也是工商心理學可以發揮貢獻的研究議題。舉例而言,針對環境的議題,已有若干研究試圖探究主管如何透過領導風格,鼓勵員工採取利環境的自發行為,並探討綠色人力資源管理(Green Human Resources Management)應如何訂定與衡量ESG的管理目標,才能讓員工在兼顧工作效能的同時,達成環境永續之目標;他們也試圖運用既有的心理學理論,說明綠色人力資源管理會透過何種機制,影響員工的幸福感、職涯規劃及勞雇關係,為最佳實務規劃與未來研究指引方向。針對社會的議題,也有不少學者運用心理學中的公平理論、偏見與歧視觀點及性別角色理論,探討如何建構一個公平、無偏見的工作環境,並實踐於企業管理實務之中。針對治理的議題,更有許多學者與實務工作者試圖探討人力資源管理如何幫助企業建構多重利害關係人治理模式(Multi-stakeholder Governance Framework),讓企業在制定策略時,能完整且全面地考量所有利害關係人的需求;同時,亦有學者從心理學理論切入,探討如何減低企業中的利組織不道德行為(Pro-organizational Unethical Behavior),避免企業陷入貪腐醜聞之中,以維護利害關係人對企業的信任。由以上觀之,從工商心理學的角度切入,探討員工在落實ESG管理目標的重要角色,可說是建構永續營運模式的重要關鍵。
基於以上所述,若能創造多元對話平台,讓學術研究者與實務工作者齊聚一堂,討論如何規劃與設計出「鼓勵與引領員工實踐ESG」的實務政策與未來研究方向,應能為落實「企業永續」之目標做出貢獻。這對追求永續實踐、致力於建構永續營運模式的企業來說,可謂別具意義。
本研討會以「企業永續:從『心』啟航」為主題,期冀透過國際學術研討會的召開,從工商心理學的視角探討企業組織如何促進員工對「企業永續」目標之認同與投入,進而落實兼顧環境、社會及治理的永續營運模式。在此基礎上,本研討會預期能透過國內外學術界與實務界的交流與對話,聚焦員工在企業永續實踐中的關鍵角色,藉此找出企業永續營運模式之可行研究方向,以及解決實務問題之有效方案。
Considering the current tides, people are faced with challenges brought by poverty, climate change, and all forms of discrimination. To counter these challenges, the United Nations has established 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in hopes of constructing a sustainable development model corresponding to the global common interest by consolidating the resources of multiple nations and uniting the forces of governments and civilians. The United Nations believes the sustainable development model should be “a model that can fulfill the needs of the current and future generations, without leaving anyone behind,” – which is a completely different approach to previous development models that heavily emphasize economic growth and short-term contentment. Therefore, other than the efforts of governments in assessing the appropriateness of current policies that stress economic development in establishing a sustainable development model that fulfills the SDGs, the ability of private enterprises transitioning from a profit-centered business model to a sustainable development model that simultaneously takes financial goals, social inclusion, and eco-friendly measures into consideration is a focal point to this discussion.
Having been affected by this trend, organizations have started to emphasize management indices that focus on environment, social, and governance (ESG) in response and to fulfill the sustainability envisioned by the SDGs. Environment-related management indices focus on whether organizations protect the environment and engage in eco-friendly behaviors while pursuing organizational interests. Social-related management indices focus on whether organizations protect labor rights – ensuring that employees of all backgrounds are treated equally, without discrimination, and are not exploited or employed wrongfully. Governance-related management indices focus on whether an organization’s top management team complies with the law and adheres to the principles of transparency by disclosing important information when necessary. As sustainable development becomes a common value, organizations that go against ESG lose stakeholders’ trust and destroy their brand image – causing major losses for the organization. For example, many financial establishments disallow their banks to finance or invest in organizations that do not adhere to ESG standards. In addition, consumers will boycott organizations that damage the environment, violate labor rights, and conceal corruption as a sign of protest. Organizations such as Google, Unilever, and Toyota are actively pushing ESG-related policies and measures – which suggest that obeying ESG protocols is a crucial factor of organization operation.
Interestingly, the success of an organization establishing a sustainable business model lies in whether employees recognize sustainability values and are willing to engage in ESG-related behaviors. In other words, how to motivate and guide employees to recognize and achieve management goals advocated by ESG is not only an unavoidable management issue but also a research topic that IO psychology can contribute to. For example, in response to environment-related management issues, there have been a few studies examining how leaders can use leadership styles to encourage employees to actively take eco-friendly measures. They have also discussed how green human resource management should set and measure ESG management goals to have employees achieve eco-friendly goals while they are striving for work efficacy. They also utilized current psychological theories to explain the underlying mechanisms behind green human resource management affecting employees’ well-being, career planning, and labor relations – providing directions for practical implication and further research. In response to social-related management issues, many researchers utilize the equity theory, perspective of stereotype, discrimination, and gender roles in discussing how to create a fair, non-biased working environment and its practical implications. In response to governance-related management issues, many scholars and practitioners examine how human resource management can create a multi-stakeholder governance framework in helping organizations set strategies that comprehensively consider the needs of all stakeholders. Also, researchers are discussing how to lower the happenings of employee pro-organization unethical behavior to avoid organizations being under corruption scandals and maintain the stakeholders’ trust towards the organization. In conclusion, examining the important role employees play in achieving ESG goals from an IO psychology perspective is the crucial key to establishing a sustainable business model.
Based on what is mentioned, if we were to create a diverse conversation platform that allows scholars and practitioners to discuss how to plan and design practical policies and future research directions on “encouraging and guiding employees in achieving ESG,” we should be able to contribute to the goal of “organization sustainability.” This will be meaningful to the organizations striving for sustainable implementation and a sustainable business model.
This year’s conference is themed “Business Sustainability: A Journey from the Heart.” From an IO psychology lens, we hope to examine how organizations can achieve a sustainable business model that focuses on the environment, society, and governance by promoting employee recognition and engagement toward organizational sustainability. Based on the points mentioned, this year’s conference hopes to reach a consensus on a plausible future research direction for sustainable business modeling and effective plans to solve practical issues through exchanges between local and international scholars and practitioners that put employees at the forefront of the conversation.



Professor Mo Wang
Warrington College of Business, University of Florida, USA
”Topic :
Working after Retirement: Psychological Forces and Environmental Constraints in Sustainable Business

Professor Ryan B. Olson
Division of Occupational and Environmental Health, The University of Utah, USA
”Topic :
First Things First: Priorities for Creating Positive and Protective Workplaces for Business Sustainability


福華國際文教會館/Howard Civil Service International House
”福華文教會館交通便捷,距離本次會議會場步行約10分鐘。會館提供安全、舒適、乾淨之住宿環境,一直以來備受台大師生肯定。
福華文教會館提供單人房、豪華套房、尊爵套房等多樣房型方案,並附設恆溫游泳池、健身中心、撞球室、桌球室等設施,讓您享受多樣的住宿體驗!
Howard Civil Service International House is conveniently located just a 10-minute walk from the conference venue. It offers a safe, comfortable, and clean environment, highly praised by NTU faculty and students.
Room options include Standard Single Rooms, Semi-Suites (2 Single Beds/ 1 Queen Size Bed). Facilities include Indoor Sunshine Temperature-Controlled Pool (with Jacuzzi), gym, billiard room, and table tennis room, ensuring a great stay.
地址/Address:台北市大安區新生南路三段三十號
No. 30, Section 3, Xinsheng South Road, Da'an District, Taipei City
電話/Tel:+886 2 77122323
福華國際文教會館/Howard Civil Service International House
會館地址:台北市大安區新生南路三段30號
捷運 :
自捷運台電大樓站2號出口,出站左轉沿辛亥路步行約10~15分鐘至辛亥路新生南路口左轉,即達福華國際文教會館。鄰近台大以及師大兩大美食及購物商圈,距離台大校園也只需步行五分鐘,享受人文以及都市的靈魂洗禮。
搭乘公車 :
龍安國小- 52,253,280,284,290,311,505,907,0南,指南1
大安森林公園- 3,15,18,52,72,74,211,235,237,278,295,626
和平新生路口- 253,280,290,311,505,642,0南,指南1,指南5
溫州街口- 3,15,18,74,235,237,254,278,295,907,291,672
公務人力發展學院- 52,253,280,284,290,291,311,505,642,907,0南,指南1
自行開車 :
中山高:下圓山交流道接建國高架→和平東路出口右轉→左轉至新生南路→右轉至辛亥路→會館地下停車場。
北二高:下木柵交流道→辛亥路過地下道直行→建國南路左轉辛亥路行駛平面車道→過新生南路交叉口→會館地下停車場。
如何前往會議場地
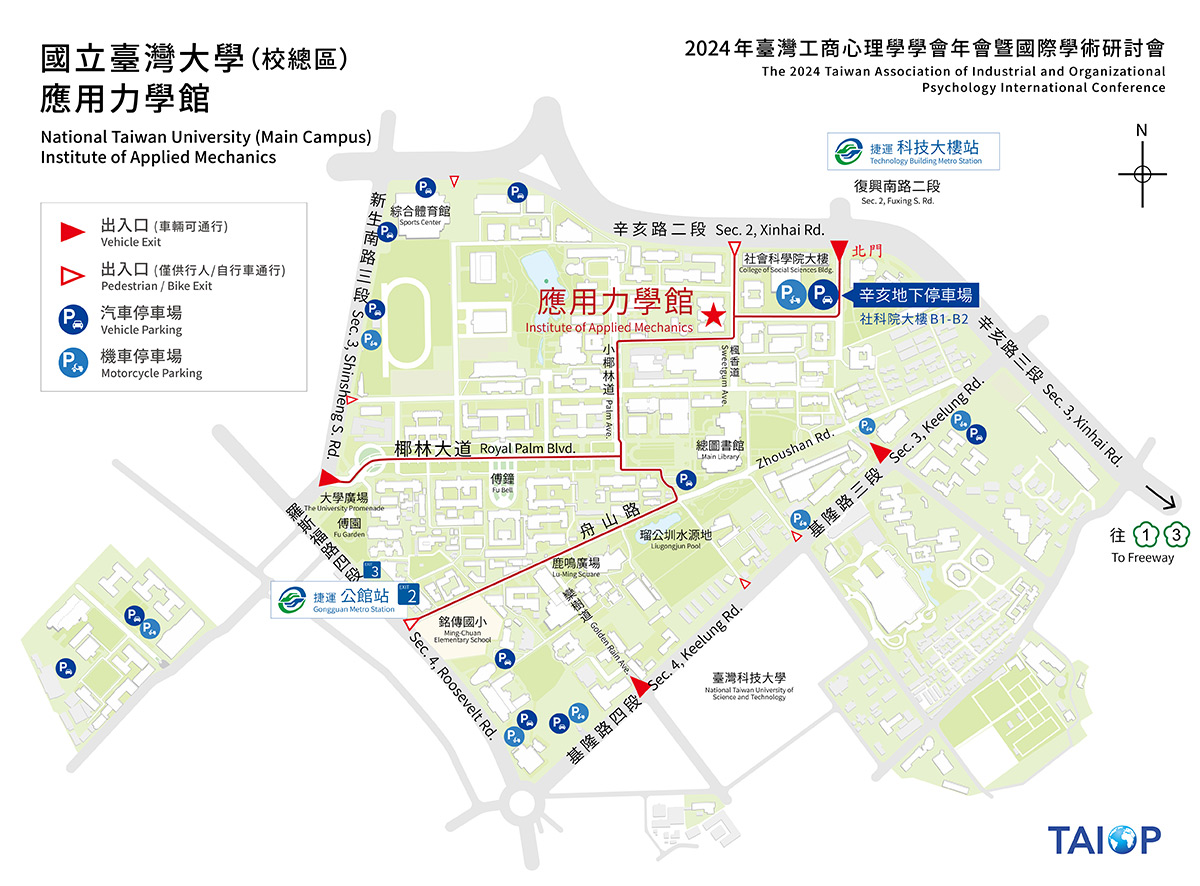
開車
- 國道1號由建國南路交流道下,走高架往南至辛亥路出口下,靠右行駛慢車道往木柵方向,至復興南路口右轉進入臺大辛亥路大門。
- 國道3號由20.8公里木柵交流道下往台北方向,接國3甲線至辛亥路,穿過基隆路車行地下道後靠右慢車道行駛至復興南路口,左邊即臺大辛亥路大門。
停車資訊
-
校園停車格 30元/30分鐘
-
辛亥地下停車場(入口:進辛亥路校門柵欄前右側,出口:辛亥路2段)
汽車:20元/30分鐘;
機車:20元/次
如何上高速公路
-
國道1號:由臺大辛亥路大門,左轉辛亥路上建國高架道。
-
國道3號:出臺大辛亥路大門,右轉辛亥路接國3甲聯絡道。
捷運
- 捷運新店線:公館站2號出口,沿舟山路過圖書館左轉,步行約13分鐘。
- 捷運文湖線:科技大樓站,沿復興南路往南走約600公尺由辛亥路校門進入後第一個路口右轉。
公車
- 臺大資訊大樓站
298、懷恩S31(於捷運公館站3號出口搭乘) - 羅斯福路公館站
30、653、74、254、278、643、644、252、251、236、 606、
291、208、1、510、253、907。 - 新生南路臺大站
642、290、505、907、284、253、52、280、311、○南,由西側門進入台大。 - 和平東路復興南路口站
3、72、74、18、52、211、235、284、237、278、15、209、295、626、和平幹線、敦化幹線。